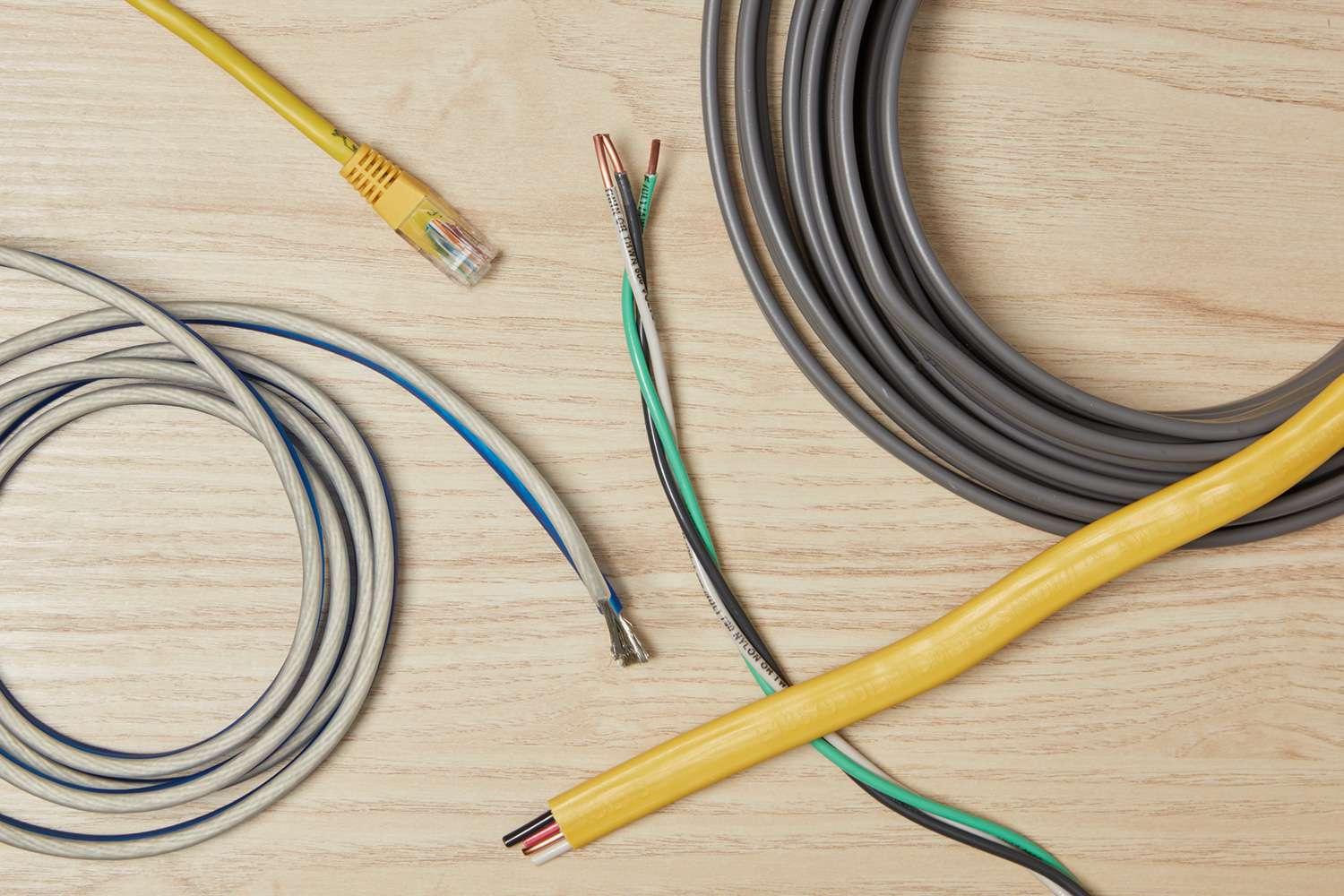
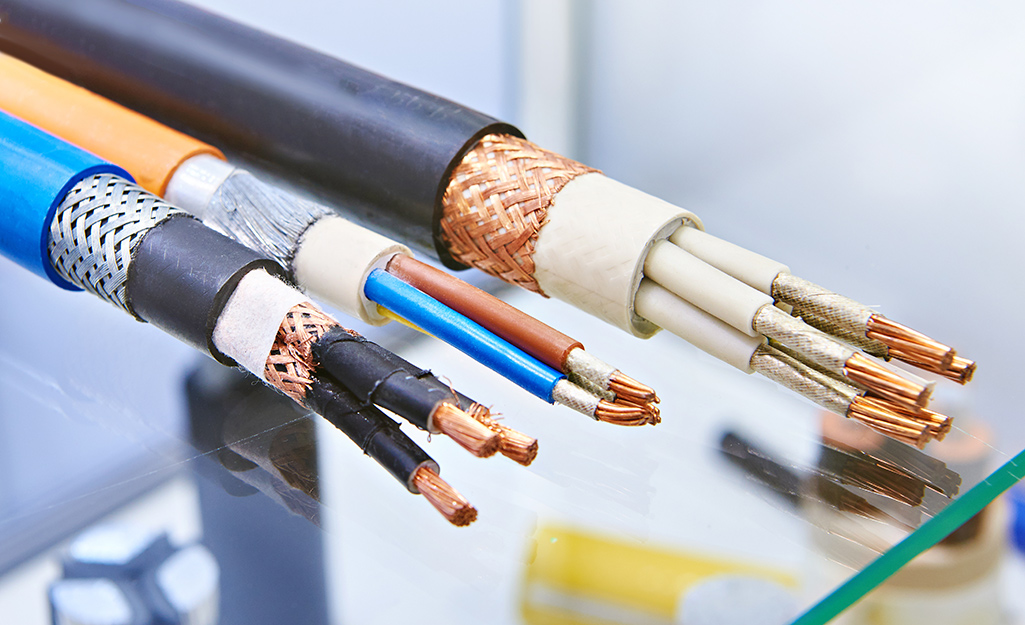
There are various types of electrical wires and cables, including single conductor wire, multi-conductor wire, single, two, and three-core cables, and armored wire. These wires are used for different purposes in electrical systems.
Introduction To Electrical Wires And Cables
Electrical wires and cables come in various types, including single conductor wire, multi-conductor wire, two and three-core cables, and armored wire. These types are used for different applications in electrical installations, providing safe and efficient transmission of electricity.
Understanding The Basics Of Electrical Wires And Cables:
Electrical wires and cables are essential components of any electrical system. They serve the purpose of carrying and distributing electrical power from one location to another. Understanding the basics of electrical wires and cables is crucial for anyone involved in electrical projects or repairs.
In this section, we will explore the different types of electrical wires and cables, their uses, and some considerations for selecting the right type for your needs.
Single Conductor Wire:
- Single conductor wire, also known as single strand wire, consists of a single conducting material, usually copper or aluminum.
- It is commonly used for low-voltage applications, such as automotive wiring or small electrical devices.
- Single conductor wire is flexible and easy to manipulate, making it suitable for installations that require bending and twisting.
Multi-Conductor Wire:
- Multi-conductor wire, also known as stranded wire, consists of multiple smaller strands of wire bundled together.
- It is commonly used for high-voltage applications, such as building wiring or industrial machinery.
- The multiple strands of wire increase flexibility and durability, making it ideal for installations that require frequent movement or vibration.
Single, Two, And Three-Core Cables:
- Single, two, and three-core cables are types of electrical cables that contain multiple conductors.
- Single-core cables have a single insulated conductor, while two and three-core cables have two or three insulated conductors respectively.
- These cables are commonly used for power distribution in residential and commercial buildings, as they allow for the simultaneous transmission of electricity to different devices or areas.
Armored Wire:
- Armored wire, also known as armored cable, is a type of electrical cable that has an additional protective layer.
- The armor layer is typically made of metal, such as steel or aluminum, and provides physical protection to the cable against mechanical damage.
- Armored wire is commonly used in industrial and outdoor applications, where the cable may be exposed to harsh environments or require protection against accidental damage.
Remember, when working with electrical wires and cables, always consult a professional or follow local electrical codes and regulations. Using the appropriate type of wire or cable for your specific application is crucial for maintaining safety and ensuring proper electrical performance.
Now that you have a basic understanding of the different types of electrical wires and cables, you can proceed to explore their characteristics and applications in more detail.
Wire Material
Wire material is an important consideration when it comes to selecting the right types of electrical wires and cables. The main options include aluminum or copper, which can be either bare or insulated with a thin layer of thermoplastic.
Exploring Different Materials Used In Electrical Wires:
Electrical wires and cables are made from different materials, each with its advantages and disadvantages. Let’s take a closer look at the most common wire materials used in electrical applications:
Copper Wire:
- Copper is one of the most widely used materials for electrical wires due to its excellent conductivity and high melting point.
- Advantages:
- Very good conductivity, allowing for efficient flow of electricity.
- High tensile strength, making it durable.
- Resistant to corrosion, ensuring long-term reliability.
- Disadvantages:
- Expensive compared to other materials.
- Can be prone to theft due to its high value.
Aluminum Wire:
- Aluminum is another popular material for electrical wires, especially in larger applications.
- Advantages:
- Lightweight, making it easier to handle and install.
- Less expensive than copper.
- Good conductivity for its weight.
- Disadvantages:
- Lower conductivity than copper, leading to higher resistance and potential heat buildup.
- More susceptible to corrosion.
- Requires larger wire sizes compared to copper for the same current-carrying capacity.
Steel Wire:
- Steel wire is often used in specialized applications such as armored cables and wire ropes.
- Advantages:
- High tensile strength, providing excellent mechanical support.
- Resistant to impact and external damage.
- Disadvantages:
- Poor electrical conductivity compared to copper and aluminum.
- Prone to rust and corrosion if not properly protected.
Fiber Optic Cable:
- Fiber optic cables use thin strands of glass or plastic to transmit data through light signals.
- Advantages:
- Immunity to electromagnetic interference.
- High bandwidth for transmitting large amounts of data.
- Lighter and more flexible than traditional wires.
- Disadvantages:
- Fragile and can break easily if mishandled.
- Requires specialized equipment for installation and termination.
Other S:
- In addition to the above materials, there are various specialized wire materials used for specific applications, such as:
- Litz wire: Consists of individually insulated strands twisted together to minimize skin effect.
- Stainless steel wire: Offers corrosion resistance and high-temperature tolerance.
- Nickel-titanium wire: Known for its shape memory properties.
- Magnet wire: Used in applications where coil winding is required.
Each wire material has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, and the choice depends on factors such as conductivity requirements, cost considerations, and environmental conditions. It is important to select the appropriate wire material to ensure safe and efficient electrical installations.
Single Conductor Wires
Single conductor wires, also known as single-strand wires, are one of the main types of electrical wires. They consist of a single, solid conductor and are commonly used for various electrical applications.
Overview Of :
Single conductor wires, also known as single-strand wires, are electrical wires that consist of a single conducting material. These wires are typically used for carrying electrical current in various applications and industries. They are designed to be flexible and easy to work with, making them suitable for a wide range of installations.
Single conductor wires are available in different sizes and gauges, allowing for flexibility in choosing the right wire for specific electrical needs.
Some key characteristics of single conductor wires include:
- Made from a single conducting material, such as copper or aluminum.
- Insulated with a protective coating to prevent electrical shocks and short circuits.
- Available in different colors to distinguish between different electrical circuits.
- Can be plain or stranded, depending on the specific application.
- Commonly used in residential, commercial, and industrial wiring projects.
Applications And Uses Of Single Conductor Wires:
Single conductor wires have a wide range of applications and are commonly used in various industries. Some of the key applications and uses of single conductor wires include:
- Power distribution: Single conductor wires are used to transmit electrical power from a power source to various electrical devices and appliances.
- Building wiring: They are used for wiring residential, commercial, and industrial buildings, providing electricity to lighting fixtures, outlets, and other electrical components.
- Automotive wiring: Single conductor wires are used in the automotive industry for wiring electrical systems in vehicles. They are used for connecting batteries, lights, sensors, and other components.
- Electronics: They are utilized in electronic devices and equipment, connecting circuit boards and providing power to different components.
- Renewable energy systems: Single conductor wires are used in solar panels, wind turbines, and other renewable energy systems to transmit electricity from the source to the grid or batteries.
- HVAC systems: These wires are used in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, connecting thermostats, motors, and other components.
Single conductor wires are versatile and essential components in electrical systems and applications. They provide a safe and efficient way to transmit electrical current and are widely used in various industries. Whether it’s for residential, commercial, or industrial purposes, single conductor wires play a crucial role in powering our modern world.
Multi-Conductor Wires
Multi-conductor wires, also known as stranded wires, are a type of electrical wire commonly used in various applications. These wires consist of multiple smaller wires twisted together, providing flexibility and enhanced conductivity. They are often used in industries such as telecommunications, electronics, and automotive for their versatility and reliable performance.
Understanding Multi-Conductor Wires:
Multi-conductor wires are cables that contain multiple insulated conducting wires within a single jacket. These wires are typically color-coded for easy identification and can vary in the number of conductors they contain. Multi-conductor wires are commonly used in various electrical applications due to their flexibility, durability, and ease of installation.
Some important points to note about multi-conductor wires include:
- Versatility: Multi-conductor wires are available in a wide range of configurations, from 2 to 50+ conductors, allowing for flexibility in different applications.
- Easy installation: With multiple conductors bundled together, multi-conductor wires simplify installation as multiple circuits can be run simultaneously, eliminating the need for separate wires.
- Space-saving: The compact design of multi-conductor wires saves space and reduces clutter in electrical installations.
- Color-coded insulation: Each conductor in a multi-conductor wire is typically insulated with a different color, making it easy to identify and distinguish between wires during installation and troubleshooting.
- Shielding options: Some multi-conductor wires come with shielding options, such as foil or braided shielding, which provide additional protection against electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI).
Benefits And Practical Applications:
Multi-conductor wires have numerous benefits and find applications in various industries. Here are some key benefits and practical applications of multi-conductor wires:
- Control and communication systems: Multi-conductor wires are commonly used for control and communication systems in industries such as manufacturing, automation, and telecommunications. They provide reliable transmission of signals and data between different components.
- Audio and visual equipment: Multi-conductor wires are widely used in audio and visual equipment, including speakers, amplifiers, microphones, and cameras. They ensure optimal signal transmission and minimize signal loss.
- Security systems: Multi-conductor wires are essential for security systems, such as CCTV cameras, alarm systems, and access control systems. They enable the seamless integration of various security components.
- HVAC systems: Multi-conductor wires are used in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems for control, power supply, and communication purposes.
- Industrial machinery: Multi-conductor wires are integral to the functioning of industrial machinery, providing power and control signals for motors, sensors, and other components.
- Automotive applications: Multi-conductor wires are utilized in automotive wiring harnesses for connecting various electrical components and systems in vehicles.
Multi-conductor wires offer versatility, ease of installation, and reliable performance. Their use is widespread across various industries for control systems, audio and visual equipment, security systems, HVAC systems, industrial machinery, and automotive applications. The color-coded insulation and shielding options make multi-conductor wires a reliable choice for efficient electrical installations.
Single, Two, And Three-Core Cables
Single, two, and three-core cables are some of the different types of electrical wires and cables used for various applications. These cables have multiple conductors and are commonly used in power distribution systems for their versatility and durability.
Differentiating Between Single, Two, And Three-Core Cables:
- Single-core cables consist of a single conducting wire insulated with a protective sheath. These cables are ideal for applications where flexibility is required, such as moving machinery or appliances. They are also used in high-voltage systems.
- Two-core cables have two conducting wires insulated separately and then sheathed together. These cables are commonly used for lighting and power circuits in residential and commercial buildings.
- Three-core cables consist of three conducting wires insulated individually and then sheathed together. They are commonly used for power transmission and distribution, as well as in industrial applications.
Suitable Applications For Each Type:
- Single-core cables:
- Power transmission in high-voltage systems
- Applications requiring flexibility, such as moving machinery or appliances
- Two-core cables:
- Lighting circuits in residential and commercial buildings
- Power circuits in homes and offices
- Three-core cables:
- Power transmission and distribution
- Industrial applications requiring a three-phase power supply
By understanding the differences between single, two, and three-core cables, you can select the right type for your specific electrical needs. Whether it’s for power transmission, lighting circuits, or industrial applications, choosing the appropriate cable type is crucial for efficient and safe electrical installations.
Remember to consult with a professional electrician if you’re unsure about the best option for your specific requirements.
Armored Wires
Armored wires, also known as armored cables, are a type of electrical wire that provides added protection through a layer of armor made of metal or other materials. They are commonly used in areas where there is a risk of damage to the wiring, such as in industrial or outdoor settings.
Exploring Armored Wires (Armored Cables):
Armored wires, also known as armored cables, are a type of electrical wiring that provides an added layer of protection. They are designed for applications where the wiring may be exposed to physical damage, such as in industrial settings or outdoor installations.
Armored cables are constructed with a metal armor layer, typically made of steel or aluminum, which encases the electrical conductors.
Advantages And Purposes Of Armored Cables:
Armored cables offer several advantages and serve various purposes in electrical installations. Here are some key points to note:
- Protection: The primary purpose of armored cables is to protect against physical damage, such as impact, abrasion, and rodent interference. The metal armor layer acts as a shield, preventing the wires from being exposed or severed.
- Durability: Armored cables are highly durable and resistant to wear and tear. The metal armor enhances the overall strength and resilience of the wiring, making it suitable for demanding applications.
- Flexibility: Despite the added protection, armored cables maintain a certain level of flexibility. This allows for easier installation, especially in areas with tight spaces or complex routing requirements.
- Waterproofing: Some armored cables come with an extra layer of insulation or sheathing material that provides moisture resistance. This feature makes them suitable for outdoor or underground installations, where exposure to water or damp environments is a concern.
- Enhanced electrical performance: The metal armor layer in armored cables also helps in reducing electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI), ensuring better signal quality and electrical performance.
- Versatility: Armored cables are available in various configurations to meet specific needs. They can be used for both power and data transmission, and are commonly found in industrial machinery, underground wiring, outdoor lighting systems, and telecommunications infrastructure.
Armored cables are a reliable solution for protecting electrical wiring in applications that require additional durability and resistance to physical damage. They offer several advantages, including enhanced protection, durability, flexibility, waterproofing, and improved electrical performance. Whether in industrial settings or outdoor installations, armored cables provide a secure and reliable solution for electrical wiring requirements.
Coaxial Cable
Coaxial cable is a type of electrical wire commonly used for transmitting high-frequency signals. It consists of a central conductor surrounded by an insulating layer, a metallic shield, and an outer insulating layer, providing excellent signal quality and low interference.
Overview And Features Of Coaxial Cables:
Coaxial cables are a type of electrical wire that consists of an inner conductor, insulating layer, metal shield, and outer protective cover. They are designed to carry high-frequency signals and have several features that make them ideal for specific applications:
- Impedance matching: Coaxial cables provide impedance matching between the source and destination, which allows for efficient signal transfer without any loss.
- Low signal loss: The metal shield of coaxial cables ensures minimal interference and signal loss, making them suitable for long-distance transmissions.
- Broadband capabilities: Coaxial cables have a wide bandwidth, making them suitable for carrying multiple signals simultaneously, such as TV, internet, and telephone signals.
- Electromagnetic shielding: The metal shield of coaxial cables protects the signal from external electromagnetic interference, ensuring a clear and uninterrupted transmission.
- Easy installation: Coaxial cables are easy to install and terminate, with connectors readily available for various applications.
Common Uses And Applications Of Coaxial Cables:
Coaxial cables have various uses and applications across different industries due to their unique characteristics. Some common uses include:
- Television and Internet distribution: Coaxial cables are widely used for transmitting television and internet signals from providers to households. They ensure high-quality video and audio transmission, making them an integral part of cable TV and internet systems.
- CCTV systems: Coaxial cables are used in closed-circuit television (CCTV) systems for transmitting video surveillance footage. The shielding of the cable protects the signal from external interference, ensuring clear and reliable video transmission.
- Radiofrequency (RF) applications: Coaxial cables are used in RF applications, such as antennas and radio transmitters. Their impedance matching and low signal loss capabilities make them suitable for carrying RF signals over long distances.
- Aerospace and defense: Coaxial cables are used in aerospace and defense industries for various applications, including communication systems, radar systems, and electronic warfare.
- Medical imaging: Coaxial cables are used in medical imaging equipment, such as ultrasound machines and MRI scanners, to transmit high-resolution image signals.
Coaxial cables provide efficient signal transmission, low interference, and wide bandwidth capabilities, making them suitable for various applications in industries such as telecommunications, surveillance, aerospace, and healthcare.
Fiber-Optic Cable
Fiber-optic cables are a type of electrical wire used for transmitting data over long distances using light signals. They offer high-speed internet connections and are resistant to interference, making them ideal for telecommunications and networking applications.
Understanding Fiber-Optic Cables:
- Fiber-optic cables are composed of thin strands of glass or plastic that transmit data using pulses of light.
- These cables are highly efficient in transmitting large amounts of data at high speeds over long distances.
- Unlike traditional copper cables, fiber-optic cables do not face interference from electromagnetic signals, resulting in clearer and faster data transmission.
Benefits And Applications In Modern Technology:
- Higher bandwidth: Fiber-optic cables have a much higher bandwidth compared to traditional copper cables, allowing for faster internet speeds and more efficient data transmission.
- Immunity to electromagnetic interference: Because fiber-optic cables use light instead of electrical signals, they are not affected by electromagnetic interference, making them ideal for high-tech environments.
- Longer distances: Fiber-optic cables can transmit data over much longer distances than copper cables without experiencing signal degradation.
- Greater data capacity: The small size and high efficiency of fiber-optic cables allow them to transmit a larger amount of data simultaneously, making them a preferred choice for applications that require high data capacity.
- Secure data transmission: Fiber-optic cables are difficult to tap into, providing a high level of security for transmitting sensitive information.
- Applications: Fiber-optic cables are widely used in telecommunications networks, internet service providers, data centers, and high-definition audio and video transmission. They are also essential for technologies such as fiber-optic internet, digital television, and teleconferencing.
With their superior capabilities and diverse applications, fiber-optic cables play a crucial role in modern technology, enabling fast and reliable data transmission in various industries.
Aluminum Building Wiring
Aluminum building wiring is one of the types of electrical wires and cables available. It is commonly used in residential and commercial buildings for electrical installations.
Exploring Aluminum Building Wiring:
Aluminum building wiring has been used in residential and commercial construction for many years. This type of wiring consists of electrical cables made primarily of aluminum conductors instead of copper. While it has its advantages, there are also important considerations to keep in mind when it comes to aluminum building wiring.
Advantages And Considerations:
Here are some key advantages and considerations when it comes to aluminum building wiring:
- Cost-effective: Aluminum wiring is generally more affordable than copper wiring, making it a cost-effective option for electrical installations.
- Lightweight: Aluminum is a lightweight material, making it easier to work with during installation compared to heavier copper wires.
- Corrosion-resistant: Aluminum wires have a natural corrosion resistance, which can extend their lifespan and reduce the risk of damage.
- High conductivity: Although aluminum has a lower conductivity than copper, it is still an effective conductor of electricity, ensuring efficient electrical flow in buildings.
- Expansion and contraction: One important consideration with aluminum building wiring is its tendency to expand and contract more than copper when exposed to temperature changes. This can lead to loose connections and potential safety hazards if not properly installed.
- Oxidation: Aluminum wiring is susceptible to oxidation, which can cause a buildup of oxide on the surface of the wire and increase resistance to electrical flow. Regular maintenance and proper connections are necessary to prevent issues related to oxidation.
- Compatibility: Aluminum building wiring may not be compatible with certain electrical devices and fixtures designed for use with copper wiring. It is important to consult with a professional electrician to ensure compatibility and safety.
- Safety precautions: Due to its unique characteristics, aluminum building wiring requires specific safety precautions during installation and maintenance. Anti-oxidant compounds, proper connectors, and regular inspections are recommended to minimize potential hazards.
Aluminum building wiring offers advantages in terms of cost and weight, but it also requires careful consideration and adherence to safety measures. It is essential to consult with a qualified electrician to determine the suitability and proper installation of aluminum wiring in your building.
Credit: www.homedepot.com
Specialized Electrical Wires
Specialized electrical wires encompass a range of types and cables, including single-conductor wire, multi-conductor wire, and armored wire. These wires are designed for specific applications and provide efficient and reliable electrical connections.
Overview Of Specialized Electrical Wires:
Specialized electrical wires are designed for specific uses and industry-specific applications. These wires are engineered to meet particular requirements, providing reliable and efficient performance in their respective applications. Whether it’s for power distribution, communication, or specialized functions, there is a wide range of specialized electrical wires available in the market.
Uses And Industry-Specific Applications:
Here are some examples of specialized electrical wires and their uses in various industries:
- Coaxial cable: This type of cable is commonly used for transmitting high-frequency signals, such as for television, internet, and CCTV systems.
- Metal Armoured cable: Armoured cables are used in applications where extra protection against mechanical damage and physical stress is required. They are commonly used in industrial environments, underground installations, and outdoor applications.
- Paired cable: Paired cables consist of two insulated wires twisted together. They are widely used in data communication systems, such as Ethernet cables for internet connections.
- Direct-buried cable: Designed for underground installations, direct-buried cables are built to withstand harsh environmental conditions and provide reliable long-distance transmission of power or data.
- Fiber-optic cable: Fiber-optic cables are used for high-speed data transmission over long distances. They are commonly used in telecommunications, internet networks, and data centers.
- Aluminum building wiring: Aluminum wires are used in electrical applications where cost-effectiveness is a priority. They are commonly used in residential and commercial buildings.
- Ribbon cable: Ribbon cables consist of multiple parallel wires that are flatly arranged. They are commonly used in computer hardware, such as connecting hard drives, disk drives, and printers.
These are just a few examples of the specialized electrical wires available in the market. Each type of wire serves a specific purpose in its respective industry and application.
Specialized electrical wires are crucial for various industries, providing reliable and efficient solutions for power and data transmission. Whether it’s for communication, power distribution, or specific applications, choosing the right specialized wire is essential to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Frequently Asked Questions On Types Of Electrical Wires And Cables
What Are The 4 Types Of Electrical Wire?
The four types of electrical wire are single conductor wire, multi-conductor wire, armored wire, and bare wire.
What Are The 3 Types Of Electrical Wires?
The three types of electrical wires are 1. Single conductor wire (single strand wire) 2. Multi-conductor wire (stranded wire) 3. Armored wire (armored cable)
What Are The 5 Types Of Electrical Wiring System?
The five types of electrical wiring systems are single conductor wire, multi-conductor wire, single, two, and three-core cables, armored wire, and insulated wire.
What Are The Different Types Of Wires In Electrical Wiring?
There are different types of wires in electrical wiring, including single conductor wire, multi-conductor wire, armored wire, and bare wire.
What Are The Different Types Of Electrical Wires And Cables?
There are various types of electrical wires and cables, including single conductor wire, multi-conductor wire, single, two, and three-core cables, and armored wire.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of electrical wires and cables is essential for any electrical project. Single-conductor wires, multi-conductor wires, cables with one, two, or three cores, and armored wires are all commonly used in various applications. It’s important to note that there are three main wires used to carry electricity: the live wire, the neutral wire, and the earth wire.
Different wiring methods, such as cleat wiring, casing and capping wiring, batten wiring, lead sheathed wiring, and conduit wiring, also play a role in electrical installations. Additionally, electric conductors can be categorized into bare wires and insulated wires, each serving specific purposes.
Whether you’re working on an indoor or outdoor project, copper or aluminum wires with or without insulation can be chosen accordingly. By familiarizing yourself with the different types of electrical wires and cables, you can make informed decisions and ensure the safety and efficiency of your electrical systems.


