Resistance welding is a process of joining metals by applying pressure and conducting an electric current through them. There are three types of resistance welding: solid state, fusion, and reflow braze.
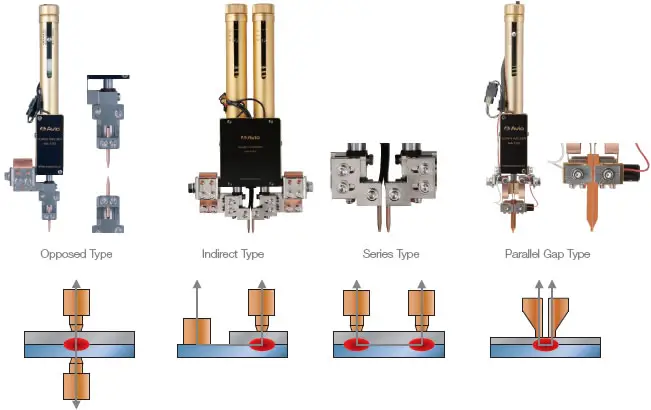
In solid-state bonding, dissimilar materials with different grain structures are joined using high weld energy, force, and a short heating time. Spot welding, which uses opposing electrodes to conduct current and apply force, is the most common form of resistance welding.
Other forms include seam welding, projection welding, flash welding, and upset welding. Resistance welding is a popular method for its efficiency and precision in joining metals.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Introduction To Resistance Welding
Resistance welding is a process of joining metal materials by applying pressure and an electric current. It includes various types such as spot welding, seam welding, projection welding, flash welding, and upset welding.
Definition And Overview Of Resistance Welding:
Resistance welding is a widely used welding process that involves the joining of metal parts through the application of heat generated by the resistance to electric current. In this process, two metal parts are brought together, with an electric current passing through them, causing localized heating at the interface.
As the metal parts are heated, they are pressed together under pressure, creating a strong and permanent weld.
Resistance welding is commonly used in various industries due to its numerous advantages, including speed, efficiency, and high-quality resulting joints. This process has different types and techniques that suit different applications, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Importance Of Resistance Welding In Various Industries:
Resistance welding plays a crucial role in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, and construction, among others. This welding process offers several benefits, which make it a preferred choice for joining metal parts in different applications.
Here are some key points highlighting the importance of resistance welding in various industries:
- Speed and Efficiency: Resistance welding enables fast and efficient joining of metal parts, leading to increased productivity in manufacturing processes. This makes it particularly suitable for high-volume production.
- Strong and Reliable Joints: The welds produced in resistance welding are known for their exceptional strength and reliability. This ensures the structural integrity of the assembled components, making them highly durable and able to withstand demanding conditions.
- Cost-effectiveness: Resistance welding often requires minimal additional materials and consumables, resulting in cost savings for manufacturers. Additionally, the efficient process reduces energy consumption, contributing to overall cost-effectiveness.
- Versatility: This welding method can be used to join a wide range of metals, including steel, aluminum, and copper. Its adaptability makes it suitable for diverse applications across multiple industries.
- Automation and Control: Resistance welding can be easily automated and controlled, allowing for precise and consistent results. This helps maintain high-quality standards while reducing human error.
- Environmentally Friendly: With no consumables or filler materials required, resistance welding is environmentally friendly. It produces minimal fumes, reducing air pollution and maintaining a clean working environment.
- Safety: Resistance welding is a relatively safe welding method compared to some other techniques. It eliminates the risk of open flames, reducing the chance of fire hazards and ensuring the safety of the operators.
Resistance welding is a versatile, efficient, and cost-effective process used in various industries for joining metal parts. Its importance lies in its ability to create strong and reliable welds, ensuring the overall quality and durability of the assembled components.
Resistance Spot Welding
Resistance spot welding is a type of resistance welding that involves joining two metal pieces together using an electric current and pressure. It is the most common form of resistance welding and is widely used in manufacturing industries.
Explanation Of Resistance Spot Welding:
- Resistance spot welding is a process in which two or more metal surfaces are joined together by applying heat and pressure. It is a type of resistance welding that is commonly used in industries for its efficiency and reliability.
- In this process, two copper electrodes are used to apply pressure and pass an electric current through the metal sheets to be joined. The resistance of the metal generates heat, melting the metal at the contact points and forming a weld.
- The welding time for resistance spot welding is typically very short, ranging from a few milliseconds to a few seconds. This makes it a fast and efficient method for joining metal components.
- The welds produced by resistance spot welding are strong and durable. They can withstand high levels of stress and are commonly used in automotive, aerospace, and construction industries.
Applications And Benefits Of Resistance Spot Welding:
- Resistance spot welding is widely used in the automotive industry for joining different components of a vehicle, such as body panels, frames, and reinforcements. It provides a strong and consistent bond, contributing to the structural integrity of the vehicle.
- This welding method is also used in the manufacturing of appliances, such as refrigerators, washing machines, and air conditioners. It helps to join various metal parts and ensures their proper functioning.
- Resistance spot welding is suitable for joining different types of metals, including steel, aluminum, and copper. It is versatile and can be used in various applications across different industries.
- Some of the benefits of resistance spot welding include:
- High production rates: It is a fast and efficient welding method, allowing for high-volume production.
- Strong and durable welds: The welds produced by resistance spot welding are highly reliable and can withstand a significant amount of stress.
- Cost-effective: This method requires minimal setup time and equipment, making it a cost-effective option for large-scale production.
- Minimal distortion: Resistance spot welding causes minimal distortion to the metal sheets, preserving the overall shape and appearance of the final product.
Advantages And Limitations Of Resistance Spot Welding:
- Advantages of resistance spot welding include:
- High productivity: It is a fast welding process that can join multiple metal sheets in a short period, increasing productivity.
- No need for filler material: Resistance spot welding does not require the use of an additional filler material, reducing costs and simplifying the welding process.
- Suitable for automation: This welding method can be easily automated, allowing for efficient and precise welding in mass production.
- Limitations of resistance spot welding include:
- Limited joint configurations: Resistance spot welding is best suited for lap joints, making it less suitable for complex joint geometries.
- Material thickness limitations: This method is most effective for joining metal sheets with thicknesses ranging from 0.5 mm to 3 mm. It may not be suitable for thicker materials.
- Surface preparation requirements: Clean and properly prepared surfaces are crucial for successful resistance spot welding. Any contaminants or oxide layers can affect the quality of the weld.
- Energy consumption: Resistance spot welding requires a significant amount of energy to generate the required heat and pressure, leading to higher energy consumption compared to other welding methods.
Electric Resistance Welding
Resistance welding is a process that joins metals together by applying pressure and a strong electric current. It encompasses various types such as spot welding, seam welding, projection welding, flash welding, and upset welding.
Understanding Electric Resistance Welding:
Electric resistance welding is a widely used welding technique that joins metals together by applying heat and pressure. The process involves passing an electric current through the metals to create heat, which then melts and fuses them. Here are some key points to understand about electric resistance welding:
- It is a fusion welding process that does not require any additional filler material.
- The heat is generated due to the resistance encountered by the electric current flowing through the metals.
- This welding method is commonly used in automotive, aerospace, and construction industries for its efficiency and reliability.
Key Features And Working Principles of Electric Resistance Welding:
The key features and working principles of electric resistance welding are as follows:
- The method is suitable for joining a wide range of metals, including steel, aluminum, copper, and brass.
- The welding process can be completed quickly and with high precision.
- It is a cost-effective method as it eliminates the need for filler materials.
- The working principle involves applying pressure between two metal surfaces while passing an electric current through them. The heat generated by the resistance melts the metal surfaces, and when the pressure is released, they solidify and form a strong weld.
Different Types Of Bonds In Electric Resistance Welding:
In electric resistance welding, different types of bonds can be formed. These bonds result from the interaction of heat and pressure during the welding process. Here are the three main types of bonds in electric resistance welding:
- Solid state bond: Also known as a thermo-compression bond, this type of bond is formed when dissimilar materials with different grain structures are joined using high weld energy, short heating time, and high force.
- Fusion bond: In a fusion bond, the metals being welded are melted and fused, resulting in a unified joint. This type of bond is commonly used in spot welding.
- Reflow braze bond: This type of bond occurs when a filler material with a lower melting point than the base metals is used during the welding process. The filler material melts and forms a bond between the base metals.
By understanding the key features, working principles, and different types of bonds, it becomes clear how electric resistance welding is a versatile and efficient method for joining metals together. Whether it is for automotive manufacturing or structural applications, this welding technique offers reliable and durable welds.
Arc Welding Methods
Resistance welding is a process where metals are joined together by applying pressure and conducting an electric current. There are different types of resistance welding methods, including spot and seam welding, projection welding, flash welding, and upset welding.
Overview Of Arc Welding Methods:
Arc welding is a type of resistance welding method that uses an electric arc to create a strong bond between metal pieces. This process involves melting the metal surfaces to be connected and allowing them to solidify, forming a durable weld.
There are several different types of arc welding methods, each with its unique characteristics and applications. Here are some of the most common arc welding methods:
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding:
- Uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to create the arc and an inert gas, typically argon, to shield the weld area.
- Suitable for welding a wide range of metals, including stainless steel, aluminum, and copper.
- Produces high-quality welds with excellent tensile strength and good control over the heat input.
Gas Metal Arc Welding:
- Also known as MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding, it uses a consumable wire electrode and a shielding gas, such as argon or a mixture of argon and carbon dioxide.
- Commonly used for welding steel, stainless steel, and aluminum.
- Offers high welding speeds and good penetration, making it a versatile method for different applications.
Submerged Arc Welding:
- Involves immersing the weld area in a granular flux to protect the arc and molten metal from the surrounding atmosphere.
- Ideal for welding thick plates and long seams in applications like shipbuilding, bridge construction, and pressure vessel fabrication.
- Provides high deposition rates and strong welds.
Carbon Arc Welding:
- Utilizes a carbon electrode to create an arc with the workpiece.
- Mostly used for welding cast iron, as it helps minimize the risk of cracking.
- Requires skill and experience to control and achieve good results.
Electroslag Welding:
- Suitable for welding thick steel plates in a single pass.
- Utilizes a consumable electrode, a molten flux, and the heat generated by an electric arc to fuse the workpieces.
- Commonly used in the construction of heavy machinery, such as crane booms and ship components.
Atomic Hydrogen Welding:
- Uses a constricted arc between two tungsten electrodes to create intense heat, and hydrogen gas to shield the area.
- Offers high-quality welds with excellent mechanical properties.
- Often used for precision welding of non-ferrous metals and alloys.
Flux-Cored Arc Welding:
- Similar to gas metal arc welding but uses a tubular electrode filled with flux instead of a solid wire.
- Provides better control over the weld and higher deposition rates.
- Suitable for welding thick materials and works well in outdoor or windy conditions.
Each of these arc welding methods has its advantages and is suited for different applications. Understanding these methods allows welders to select the most appropriate technique for their specific needs.
Other Types Of Resistance Welding
Resistance welding encompasses various types, including spot welding, seam welding, projection welding, flash welding, and upset welding. These techniques involve applying pressure and conducting an electric current to join metals together, making them highly effective for industrial applications.
Resistance welding is a popular method used in various industries to join metal pieces together. In addition to spot welding, other types of resistance welding offer unique advantages and applications. Let’s explore some of these types below:
Solid State Welding:
- This type of resistance welding involves joining materials without melting them.
- The metal pieces are compressed together under high pressure, generating heat through friction and deformation.
- Solid-state welding is commonly used for joining materials that are difficult to weld using other methods, such as aluminum and stainless steel.
Oxy-Fuel Welding And Cutting:
- Oxy-fuel welding utilizes a mixture of oxygen and fuel gas, such as acetylene, to create a flame that melts the metal pieces to be joined.
- This type of resistance welding is frequently used for cutting metals as well.
- Oxy-fuel welding and cutting are commonly employed in the fabrication and repair of metal structures, pipelines, and automotive components.
Exothermic Welding:
- Exothermic welding, also known as thermite welding, involves a chemical reaction between a powdered metal and a metal oxide.
- This reaction generates intense heat that melts the metals and forms a strong bond when they solidify.
- Exothermic welding is often used for grounding electrical connections, such as for railway tracks, telecommunication towers, and power substations.
Laser Beam Welding:
- Laser beam welding utilizes a high-intensity laser beam to heat and melt the metal pieces, forming a weld.
- It offers precise control and minimal heat-affected zones, making it suitable for welding thin and delicate materials.
- Laser beam welding finds applications in the automotive, aerospace, and electronics industries.
Butt Welding:
- Butt welding involves joining two metal pieces by placing their ends together and applying pressure and heat to create a weld.
- It is commonly used for joining pipes, tubes, and sheet metal.
- Butt welding provides high-quality, strong welds, making it popular in construction, manufacturing, and plumbing industries.
These various types of resistance welding offer unique advantages and are suitable for different applications. From solid-state welding that doesn’t involve melting to laser beam welding with precise control, each method caters to specific needs in various industries. By choosing the right type of resistance welding, manufacturers can ensure strong and reliable joints for their metal products.
Examples Of Resistance Welding
Resistance welding encompasses various types of bonds, including solid state, fusion, and reflow braze. Spot welding is the most common form, where opposing electrodes apply pressure and welding current to create each weld. Other forms include seam, projection, flash, and upset welding, distinguished by the types and shapes of weld electrodes used.
Various Examples Of Resistance Welding Applications:
- Automotive industry: Resistance welding is widely used in the automotive industry for joining components like body panels, chassis, and frame structures.
- Aerospace industry: It plays a crucial role in joining aircraft structural components, such as wings, fuselage, and engine parts.
- Electrical industry: Resistance welding is used for connecting wires, cables, and electrical components, ensuring secure connections.
- Consumer goods manufacturing: It is employed for joining metal parts in the production of appliances, furniture, and various household items.
- Construction industry: Resistance welding finds applications in the fabrication of steel structures, bridges, and pipelines.
- Medical industry: It is utilized for joining medical instruments, surgical devices, and implants, ensuring precision and reliability.
Real-World Scenarios Where Resistance Welding Is Used:
- Resistance spot welding: This method is commonly used for joining two or more metal sheets, making it ideal for automotive body assembly.
- Resistance seam welding: It is employed for sealing and joining long seams in fuel tanks, pipes, and pressure vessels.
- Flash butt welding: This technique is used in the rail and wire industries for joining rails, wires, and bars by creating a high-quality, solid-state bond.
- Projection welding: It is commonly utilized in the manufacturing of metal fasteners, such as nuts, bolts, and studs.
- Resistance butt welding: This method is used for joining similar or dissimilar metal bars, rods, and pipes in various industries.
- Percussion welding: It is used for joining dissimilar materials, such as aluminum to copper, in industries like automotive and electronics.
Benefits and practical advantages of resistance welding:
- High-quality welds: Resistance welding produces strong and reliable welds with minimal or no defects, ensuring structural integrity.
- Fast cycle times: The process is relatively quick, reducing production time and increasing efficiency.
- Cost-effective: Resistance welding requires minimal consumables and has lower operational costs compared to other welding methods.
- Environmentally friendly: It produces less smoke, fumes, and hazardous byproducts, making it a cleaner and safer option.
- Versatile: Resistance welding can be applied to a wide range of metals and alloys, making it suitable for various industries and applications.
- Automation-friendly: It can be easily integrated into automated production lines, enhancing productivity and consistency.
Common Questions About Resistance Welding
Resistance welding is a process that joins metals by applying pressure and conducting an electric current to heat and melt the welding joint. The three basic types of resistance welding bonds are solid state, fusion, and reflow braze. The most common form of resistance welding is spot welding.
Resistance welding is a type of welding that involves the use of electric resistance to create heat and bond two materials together. It is widely used in various industries for its efficiency, speed, and reliability. If you’re new to resistance welding or simply looking for more information, we have compiled a list of commonly asked questions to help you understand the process better.
Faqs Related To Resistance Welding And Its Types:
- What is resistance welding?
- Resistance welding is a welding process that relies on the heat generated by the resistance of the materials being joined to facilitate bonding.
- What are the types of resistance welding?
- Spot welding: This is the most common form of resistance welding, where opposing electrodes conduct and concentrate welding current to form each weld.
- Seam welding: It involves welding along a continuous joint or seam, typically used for joining sheets of metal.
- Projection welding: In projection welding, small projections on one or both of the materials being welded help concentrate the heat and pressure for a stronger bond.
- How does resistance welding work?
- In resistance welding, an electric current passes through the materials being welded, generating heat due to their resistance. The heat melts the interface between the materials, creating a molten pool that solidifies to form the weld.
Answers To Commonly Asked Questions About Resistance Welding:
- What is the most common form of resistance welding?
- Spot welding is the most common form of resistance welding. It involves joining two or more metal sheets by applying pressure and heat at specific spots using electrodes.
- What are the advantages of resistance welding?
- Resistance welding offers several benefits, including high productivity, excellent weld quality, reduced heat distortion, and the ability to join a wide range of materials.
- Is resistance welding suitable for all materials?
- Resistance welding is best suited for materials that are electrically conductive, such as metals and alloys. Non-conductive materials like plastics cannot be joined using this welding process.
Troubleshooting Common Issues In Resistance Welding:
- What are the common problems encountered in resistance welding?
- Poor weld quality: This can result from insufficient heat or pressure, improper electrode alignment, or contaminants on the workpiece surface.
- Electrode wear: Continuous welding can lead to electrode degradation, which can affect the quality of the welds.
- Electrical problems: Issues with current, voltage, or transformer settings can impact the welding process.
- How can I troubleshoot welding issues in resistance welding?
- Ensure proper electrode alignment and clean workpiece surfaces.
- Check for the correct current and voltage settings.
- Monitor electrode wear and replace worn electrodes.
- Regularly maintain and clean welding equipment.
Remember, resistance welding can vary based on specific applications, materials, and equipment used. It is always recommended to consult professionals or refer to equipment manuals for detailed instructions and troubleshooting tips.
Frequently Asked Questions For What Is Resistance Welding And Its Types
What Is An Example Of Resistance Welding?
Resistance spot welding is an example of resistance welding. It involves applying pressure and an electric current to join metals together.
What Are The 3 Basic Types Of Resistance Welding Bonds?
The three basic types of resistance welding bonds are solid state, fusion, and reflow braze.
What Is The Most Common Resistance Welding?
The most common form of resistance welding is spot welding. It uses opposing electrodes to conduct welding current and apply forging force for each weld.
What Is Another Name For Resistance Welding?
Another name for resistance welding is electric resistance welding (ERW).
Q: What Are The Different Types Of Resistance Welding?
A: The different types of resistance welding include spot welding, seam welding, projection welding, flash welding, and upset welding.
Conclusion
Resistance welding is a versatile and efficient method of joining metals that offers several types – spot welding, seam welding, projection welding, flash welding, and upset welding. Each type has its unique characteristics and applications. Spot welding is the most common form of resistance welding and is widely used in automotive and construction industries.
Seam welding is suitable for creating continuous welds in sheet metal assemblies. Projection welding is used for joining parts with protrusions or projections. Flash welding is commonly used for larger, irregularly shaped components. Upset welding is ideal for creating strong joints in wires or rods.
Overall, resistance welding is a reliable and cost-effective method that provides strong and durable welds. It offers excellent control over welding parameters and produces consistent results. By understanding the different types of resistance welding and their applications, you can select the most appropriate technique for your specific needs.
So, whether you are in the automotive, construction, or any other industry that requires metal joining, resistance welding is a reliable choice that ensures efficient and durable results.