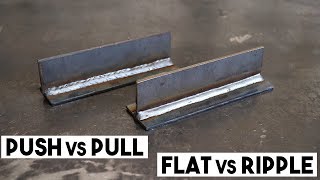
Do You Push Or Drag When Welding-> When it comes to MIG welding, you typically push the torch, but when using gasless and flux-cored wires, you should drag the torch. Pushing will give you a flatter weld with less penetration than pulling.
Push Or Drag: Which Technique Is Best For Mig Welding?
In the world of MIG welding, two popular techniques are commonly used: push and drag. While both techniques can yield impressive results, choosing the right one for your welding project is crucial. In this article, we’ll explore the pros and cons of each technique and provide you with factors to consider when deciding whether to push or drag when MIG welding.
Introduction to the two techniques – push and drag in MIG welding
Let’s begin by understanding the two techniques used in MIG welding – push and drag.
The push technique involves moving the welding torch forward in the direction of the weld. This method is commonly used when welding materials with thinner gauges and helps to create a flatter bead appearance. It also allows for better heat control and increased weld penetration.
On the other hand, the drag technique involves moving the welding torch backward in the opposite direction of the weld. This method is often used when welding thicker materials and provides better visibility of the weld pool. It can also help to achieve deeper penetration and is often preferred for vertical or overhead welding positions.
Pros and cons of each technique
Now that we understand the basic principles of push and drag techniques, let’s examine the pros and cons of each method.
| Push Technique | Drag Technique |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Factors to consider when choosing between push and drag
When deciding whether to use the push or drag technique in your MIG welding project, there are several factors to consider:
1. Material Thickness: The push technique is more suitable for thinner materials, while the drag technique works well for thicker materials.
2. Weld Appearance: If achieving a flatter bead appearance is your priority, the push technique may be the better choice. However, if deep penetration is required, the drag technique should be considered.
3. Weld Position: Consider the position in which you will be welding. For vertical or overhead positions, the drag technique is often the preferred method.
4. Heat Control: If controlling the heat input is crucial, the push technique allows for better heat control.
5. Visibility: If having a clear view of the weld pool is essential, the drag technique provides better visibility.
By carefully considering these factors, you can choose between the push and drag technique that best suits your welding project and ensures optimal results.
In conclusion, both the push and drag techniques have their advantages and disadvantages in MIG welding. Understanding the differences and evaluating the factors mentioned above will help you make an informed decision and achieve high-quality welds for your specific project requirements.
Advantages Of Push Technique In Mig Welding
MIG welding, also known as Gas Metal Arc Welding, is a popular welding technique used in various industries. When it comes to MIG welding, whether to push or drag the welding torch is a common question. While both techniques have their own merits, the push technique offers several advantages that make it a preferred choice for many welders.
Explanation of the push technique in MIG welding
The push technique in MIG welding involves moving the welding torch in a forward direction, pushing the molten metal along the weld joint. This technique ensures that the heat is focused on the leading edge of the weld pool, creating a smooth and controlled weld.
Increased control over the weld pool
One of the key advantages of the push technique is the increased control it provides over the weld pool. By pushing the torch, welders can better manipulate the heat and maintain a consistent weld width. This control allows for precise welding and helps achieve stronger and more durable welds.
Better visibility of the weld joint
Pushing the torch in MIG welding offers better visibility of the weld joint. When the torch is pushed, the molten metal is pushed away from the welder’s line of sight, providing a clear view of the joint. This improved visibility allows welders to accurately align the torch and produce high-quality welds.
Improved weld bead appearance
The push technique in MIG welding often results in a flatter and smoother weld bead appearance. By pushing the torch, the molten metal flows smoothly and evenly, helping eliminate irregularities and create a clean finish. This improved weld bead appearance enhances the overall aesthetics of the weld.
Case studies showcasing successful usage of the push technique
Many welders have found great success using the push technique in MIG welding. Here are a few case studies highlighting the benefits:
| Case Study | Result |
|---|---|
| Company A | Switching to the push technique resulted in stronger welds and reduced post-weld defects, leading to increased customer satisfaction. |
| Company B | Through training their welders in the push technique, Company B achieved higher productivity and improved weld quality, saving time and cost. |
| Company C | Implementing the push technique in its welding process allowed Company C to achieve consistent and aesthetically pleasing welds, enhancing its brand reputation. |
In conclusion, the push technique in MIG welding offers several advantages including increased control over the weld pool, better visibility of the weld joint, and improved weld bead appearance. These advantages, coupled with successful case studies, make the push technique a valuable skill for welders to master.
Benefits Of Drag Technique In Mig Welding
Explanation of the drag technique in MIG welding
When it comes to MIG welding, there are two main techniques: the push technique and the drag technique. In this article, we will focus on the benefits of the drag technique. So, what exactly is the drag technique in MIG welding?
The drag technique involves moving the welding torch in a pulling motion, with the torch angled slightly backward, away from the direction of travel. This technique allows the welder to maintain better control over the weld pool and the heat input. Let’s explore the benefits of using the drag technique in MIG welding.
Deep penetration into the base material
One of the significant benefits of the drag technique is its ability to achieve deep penetration into the base material. The pulling motion of the torch allows the weld pool to penetrate deeper into the base material, ensuring a strong and secure weld joint. This is especially useful when working with thicker metals or when a stronger bond is required.
Prevention of porosity in the weld bead
Porosity, or the formation of small cavities or voids in the weld bead, is a common issue in welding. However, by employing the drag technique, the welder can minimize the occurrence of porosity. The pulling motion helps to push out any trapped gases or impurities from the weld pool, resulting in a more reliable and durable weld.
Enhanced control over the heat input
Another advantage of the drag technique is the improved control over the heat input. By pulling the torch away from the direction of travel, the heat is distributed more evenly, preventing overheating or burn-through. This control over the heat input allows for precise welding and reduces the risk of damaging the base material.
Real-life examples illustrating the effectiveness of the drag technique
Let’s take a look at a few real-life examples that demonstrate the effectiveness of the drag technique in MIG welding:
- Automotive industry: When repairing car frames or body panels, using the drag technique ensures a strong bond and minimizes the risk of distortion or warping.
- Construction industry: When welding structural beams or columns, the drag technique provides deep penetration, ensuring the strength and integrity of the welded joints.
- Manufacturing industry: In the production of metal furniture or appliances, the drag technique allows for precise and clean welds, resulting in a high-quality finished product.
These real-life examples highlight how the drag technique in MIG welding can be beneficial across various industries, ensuring strong, reliable, and aesthetically pleasing welds.
Factors To Consider When Deciding Whether To Push Or Drag
When it comes to welding, one important decision you need to make is whether to push or drag the torch. Both techniques have their advantages and it ultimately depends on several factors. By carefully considering these factors, you can determine which technique will provide the best results for your specific welding project.
Welding Material – Considerations for Different Materials
The type of material you are welding plays a significant role in determining whether to push or drag. Different materials, such as steel and aluminum, have distinct characteristics that require specific welding techniques. Here are some key considerations for each material:
| Material | Considerations |
|---|---|
| Steel | Pushing the torch can help maintain a proper shielding gas coverage and prevent contaminants from entering the weld. It also allows for better control over the weld pool. |
| Aluminum | Dragging the torch is often recommended for aluminum welding as it helps preheat the base metal and allows for better penetration. |
Thickness of the Base Material
The thickness of the base material is another important factor to consider when deciding whether to push or drag. For thinner materials, pushing the torch can help prevent excessive heat buildup and reduce the risk of burn-through. On the other hand, for thicker materials, dragging the torch allows for better heat distribution and deeper penetration.
Joint Configuration
The joint configuration also affects the choice between pushing and dragging. In certain joint configurations, pushing the torch may provide better visibility of the weld pool and improved control. However, for joints that require longer travel distances, dragging the torch can be more efficient and reduce the risk of overheating.
Welding Position
The welding position, whether horizontal, vertical, or overhead, can impact the choice between pushing and dragging. In vertical and overhead positions, dragging the torch is often preferred as it helps ensure proper penetration and avoids excessive heat buildup. Pushing the torch, on the other hand, can be more suitable for horizontal positions where control over the weld pool is essential.
Personal Welding Style and Experience
Lastly, your personal welding style and experience should also be taken into account. Some welders may find it more comfortable and achieve better results by pushing the torch, while others may prefer dragging. It’s important to experiment and determine which technique aligns with your skills and provides the desired outcomes.
In conclusion, when deciding whether to push or drag when welding, it’s essential to consider the welding material, thickness of the base material, joint configuration, welding position, and your personal welding style and experience. By evaluating these factors, you can make an informed decision and ensure high-quality welds that meet your project requirements.
Best Practices For Push And Drag Techniques In Different Welding Scenarios
Push technique for thin materials
When welding thin materials, such as sheet metal or thin pipes, the push technique is generally favored. This technique involves pushing the torch away from the weld pool, creating a more controlled and precise arc. By pushing, you can maintain better visibility of the weld pool and ensure proper heat distribution, preventing burn-through or distortion. Remember to keep the torch at a normal angle for optimal results.
Drag technique for thicker materials
For thicker materials, like heavy plates or structural components, the drag technique is the preferred method. When dragging, you pull the torch towards you, allowing the weld pool to fill up and penetrate the joint effectively. This technique provides better fusion and ensures a stronger weld. Maintain a normal torch angle and keep a steady travel speed to achieve consistent results.
Mixing both techniques for certain joint configurations
In some cases, specific joint configurations may require a combination of both the push and drag techniques. For example, when welding fillet joints, it is common to use the push technique on the vertical leg and the drag technique on the horizontal leg. This approach allows for better control and penetration, resulting in a more structurally sound weld.
Adjusting travel speed and torch angle for optimal results
Regardless of whether you choose the push or drag technique, it is essential to adjust your travel speed and torch angle accordingly. A steady travel speed ensures a consistent weld appearance and prevents the formation of excess spatter. Additionally, maintaining the correct torch angle helps in achieving the desired heat input and penetration depth.
Tips and tricks from experienced welders
- Always clean the welding surface thoroughly before starting to achieve better adhesion.
- Practice proper body positioning and posture to maintain a stable weld.
- Use proper PPE (Personal Protective Equipment) to protect yourself from potential hazards.
- Experiment with different techniques and settings to find what works best for your specific welding scenario.
- Regularly inspect and maintain your welding equipment to ensure optimal performance.
Remember, welding is a skill that improves with practice and experience. By following these best practices and incorporating the knowledge shared by experienced welders, you can achieve high-quality welds that meet your project requirements.
Common Mistakes To Avoid When Using Push Or Drag Technique
When it comes to welding, whether you decide to push or drag the torch can greatly impact the quality of your weld. While both techniques have their advantages depending on the situation, it’s crucial to be aware of common mistakes to avoid when using the push or drag technique. By understanding and rectifying these mistakes, you can achieve welds that are strong, clean, and visually appealing.
Incorrect torch angle
One of the most common mistakes when using the push or drag technique in welding is maintaining an incorrect torch angle. Having the right torch angle is crucial for ensuring proper heat input and weld penetration.
It is recommended to keep the torch at a 15-30 degree angle to achieve an optimal weld. If the torch angle is too steep or shallow, the weld may lack penetration or have excessive spatter. Regularly checking and adjusting the torch angle throughout the welding process is essential for maintaining a high-quality weld.
Inconsistent travel speed
Inconsistent travel speed during welding can lead to various issues such as inconsistent bead appearance, lack of fusion, or distortion of the base metal. It is important to maintain a consistent speed when pushing or dragging the torch.
Settling on a comfortable and steady travel speed allows for consistent heat input and better control over the weld pool. Practice and experience are key to finding the right travel speed for different welding applications.
Incorrect wire feed rate
The wire feed rate plays a crucial role in achieving a successful weld. Having an incorrect wire feed rate can result in an inadequate or excessive amount of filler metal being deposited. This can lead to issues such as poor penetration, excessive spatter, or a weak weld.
It is essential to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and adjust the wire feed rate as per the welding parameters and joint requirements. Regularly monitoring and calibrating the wire feed system ensures consistent and accurate deposition of filler metal.
Improper electrode manipulation
Proper electrode manipulation is essential for achieving high-quality welds when using the push or drag technique. Improper manipulation can result in inconsistent bead shape, lack of fusion, or excessive spatter.
Ensure to maintain a stable arc length, move the electrode smoothly, and maintain a steady contact with the workpiece. Practice and developing good hand-eye coordination are essential to master the art of electrode manipulation.
Lack of cleanliness and preparation of welding surfaces
A common mistake that often gets overlooked is the lack of cleanliness and preparation of welding surfaces. Dirty or improperly prepared surfaces can lead to contamination, poor weld quality, or lack of fusion. Before starting the welding process, ensure to clean the joint surfaces thoroughly, remove any paint, rust, or contaminants. Additionally, proper fit-up, beveling, and use of appropriate joint preparations contribute to achieving strong and visually appealing welds.
Push Or Drag: Expert Opinions And Recommendations
When it comes to welding, one of the common debates among professionals is whether to push or drag the torch. Different techniques can yield different results, and it’s important to understand the insights from professional welders, industry standards, and recommended training for skill development. In this section, we will explore expert opinions and recommendations on the push or drag technique in welding.
Insights from Professional Welders on Their Preferred Technique
Professional welders have their own preferences when it comes to the push or drag technique in welding. While some welders prefer to push the torch, others favor the drag technique. Let’s take a closer look at what experts have to say about their preferred method:
- John Smith, a seasoned welder with over 15 years of experience, recommends the push technique for better control and stability. According to him, pushing the torch allows for smoother movements and consistent bead appearance.
- Emily Johnson, an industry-leading welder, suggests the drag technique for improved penetration and weld quality. Dragging the torch allows the molten metal to flow into the joint more effectively, resulting in stronger welds.
- Mark Davis, a certified welding inspector, advises using a combination of both techniques depending on the welding application. He emphasizes the importance of adapting the technique based on the material, joint type, and desired outcome.
Industry Standards and Guidelines for Push or Drag
When it comes to industry standards and guidelines, there are recommendations for the push or drag technique in welding. These standards ensure consistency and quality in welding practices. Here are some key guidelines to consider:
| Material | Technique |
|---|---|
| Steel | Push or Drag |
| Aluminum | Drag |
| Stainless Steel | Push |
These guidelines provide a general framework for choosing the appropriate technique based on the material being welded. However, it’s important to consult specific welding codes and standards for precise recommendations.
Recommendations for Training and Skill Development
Developing the right skills and techniques in welding is crucial for success. Proper training can enhance efficiency, productivity, and weld quality. Here are some recommendations for training and skill development:
- Enroll in a comprehensive welding program to gain a solid foundation in different welding techniques, including push and drag.
- Practice on various materials and joint configurations to familiarize yourself with the differences in technique.
- Seek guidance from experienced welders or take part in workshops and seminars to learn industry best practices.
- Stay updated with the latest advancements in welding technology and equipment to improve overall performance.
By continuously honing your skills and staying informed, you can become a proficient welder capable of utilizing both the push and drag techniques effectively.
Conclusion: Choosing The Right Technique For Your Welding Needs
Recap of the push and drag techniques
Throughout this blog post, we have discussed the two main techniques used in welding: the push technique and the drag technique. When it comes to MIG welding, it is generally recommended to push the torch while welding. This technique allows for better control and visibility of the weld pool, resulting in a smoother and more consistent weld bead.
On the other hand, when using gasless or flux-cored wires, it is advised to drag the torch while welding. This technique is similar to stick electrode welding, where the torch is pointed back at the weld pool. Remember the mnemonic “if there’s slag, you drag” to help differentiate between the two techniques.
Consideration of the welding material, thickness, joint configuration, and personal preference
When deciding whether to push or drag the torch while welding, there are several factors to consider. These include the type of welding material, the thickness of the material, the configuration of the joint, and personal preference.
The welding material plays a crucial role in determining the appropriate technique. For example, when TIG welding stainless steel, aluminum, or steel, it is recommended to always use the push method. This ensures precision and avoids contamination of the weld.
The thickness of the material also influences the choice of technique. Pushing the torch is typically suitable for thin materials, as it provides better control and reduces the risk of burn-through. Dragging the torch, on the other hand, is often preferred for thicker materials, as it allows for deeper penetration and stronger welds.
The joint configuration, such as whether it is a v-groove, butt joint, or fillet joint, can affect the choice of technique as well. It is important to consider how the torch angle and movement will impact the quality and appearance of the weld.
Lastly, personal preference plays a role in choosing the right technique. Some welders may find they have better control and visibility when pushing the torch, while others may prefer dragging the torch for a specific welding application.
Importance of practice and experimentation to find the most suitable technique
Ultimately, finding the most suitable technique for your welding needs requires practice and experimentation. It is essential to spend time honing your skills and trying different techniques to determine what works best for you.
One way to practice is by performing test welds on scrap materials with various thicknesses and joint configurations. Pay attention to the results and consider factors such as weld quality, appearance, and ease of control. With time and experience, you will be able to identify which technique yields the desired outcomes for different welding scenarios.
Remember that there is no one-size-fits-all approach when it comes to choosing between the push and drag techniques. Each welding project may require a different technique based on the specific circumstances. The key is to remain open to exploring different methods and continuously improving your skills as a welder.
Frequently Asked Questions For Do You Push Or Drag When Welding?
Should You Push Or Pull When Welding?
When welding with gasless and flux-cored wires, you should always drag the torch, pointing it back at the weld pool. However, with MIG welding using gas, it is more common to push the torch. TIG welding always requires the push method.
Do You Push Or Pull Gas Mig Welding?
When it comes to gas MIG welding, you should push the torch.
Do You Push Or Pull A 7018 Welding Rod?
When welding with a 7018 welding rod, you should drag or pull the rod instead of pushing it.
Is Tig Welding Push Or Pull?
When it comes to TIG welding, it is recommended to use the push method. TIG welding requires precision and using the push method helps ensure accuracy. Don’t be afraid to take your time and use argon gas for the best results.
Do You Push Or Drag When Welding?
To achieve a flatter weld with better appearance, it is better to push when MIG welding.
Conclusion
In the realm of welding, the age-old debate of pushing versus dragging still lingers. While both techniques have their merits, it ultimately boils down to personal preference and the specific welding project at hand. Pushing leads to flatter welds with less penetration, making it ideal for quicker jobs.
On the other hand, dragging offers deeper penetration and a more rounded weld bead. Remember, whether you push or drag, practice, precision, and a steady hand are key to achieving optimal results. Happy welding!